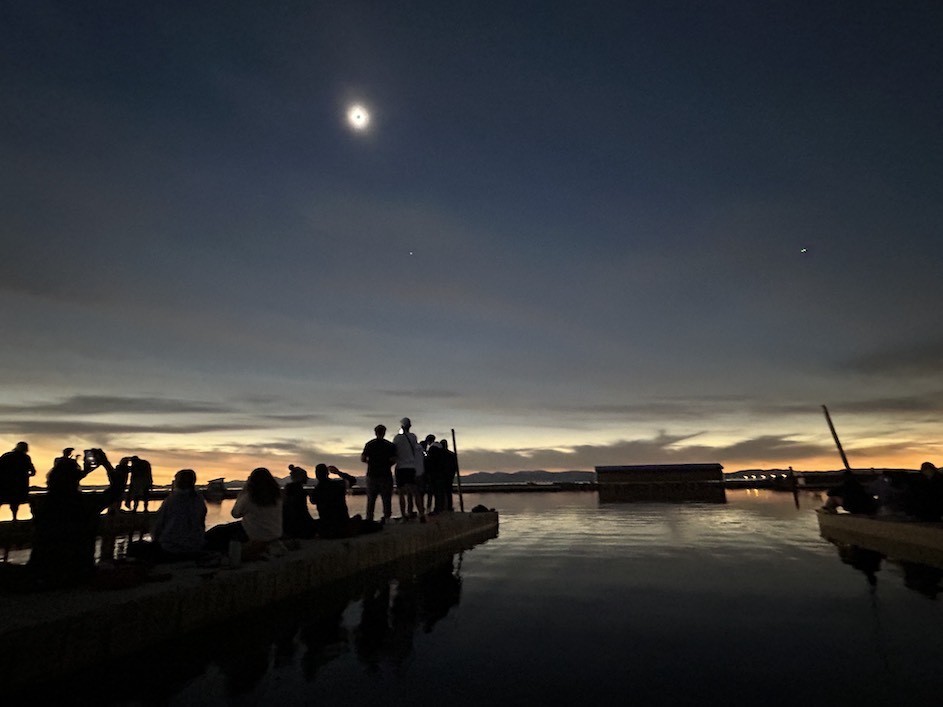
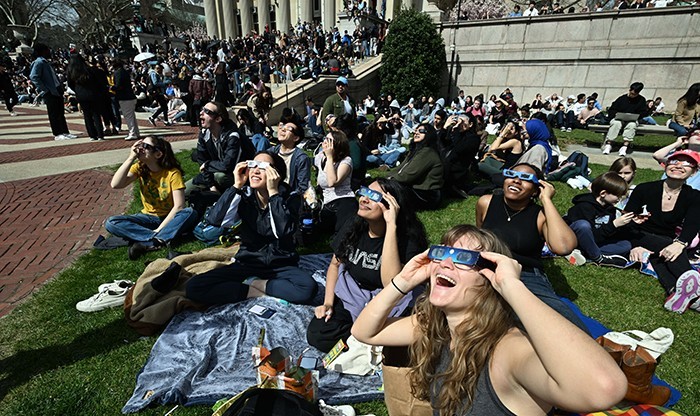
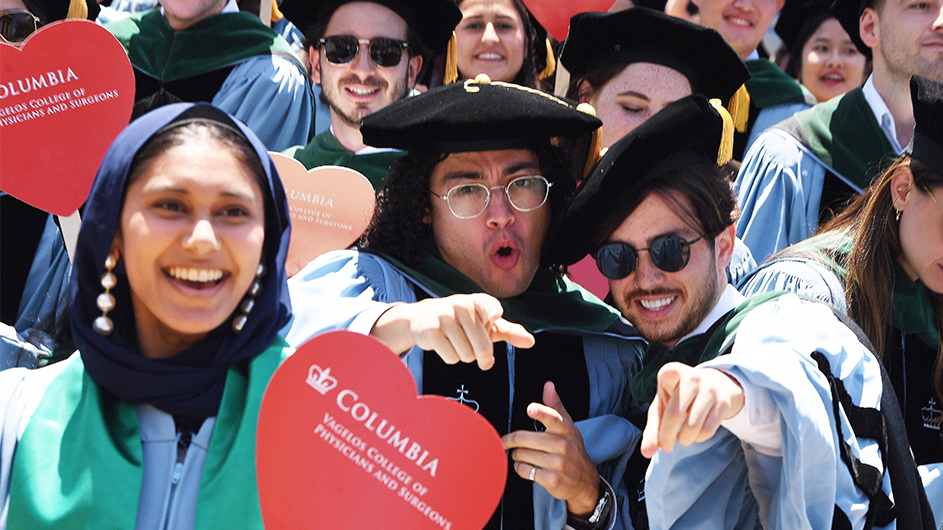
EVENTS
Upcoming
Ongoing
Locations

116th and Broadway
New York, NY 10027
212-854-1754
Intercampus Shuttle

125th and Broadway
New York, NY 10027
212-854-1754
Manhattanville Loop Shuttle

61 Rte. 9W
Palisades, NY 10964
845-359-2900
Shuttle Service
Community

Columbia Neighbors is part resource guide, part community news and storytelling hub, part gathering place. It is for everyone in the communities surrounding our campuses in Upper Manhattan.
The Office of Government and Community Affairs is the University’s primary liaison with federal, state, and local government, as well as with residents, community leaders, and civic organizations in surrounding neighborhoods. The CUIMC Office of Government & Community Affairs maintains a similar role for communities surrounding the Irving Medical Center.















.jpg?itok=ftTX9X6W)